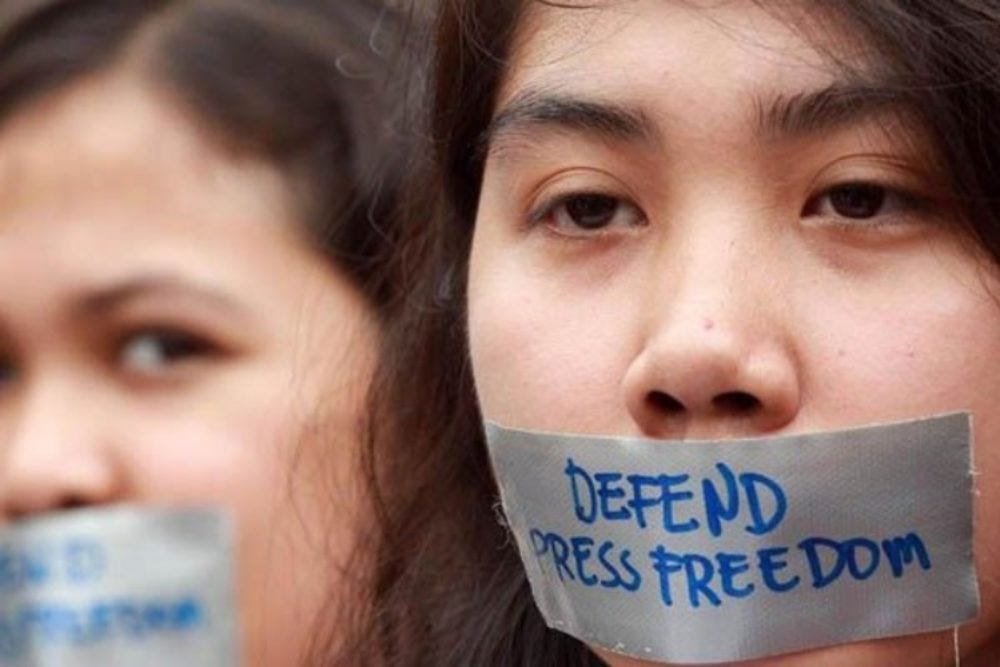
Freedom of the press, a revolutionary idea pioneered in Britain by courageous government critics in the 1720s and then enshrined in the American Bill of Rights in 1791, is under extraordinary assault at home in the United States and elsewhere. That’s no wonder; the right to free expression threatens politicians everywhere who equate criticism of them with criticism of all that’s right and proper.
Of course, the assault is driven partly by ego — “L’etat, c’est moi,” said King Louis XIV, a phrase echoed in various forms by Donald J. Trump and his imitators (see Ron DeSantis) who seek to tame a rambunctious press. And, in places such as Russia and China, it reflects longstanding state policy that lately is growing more troublesome. Elsewhere, the threats to journalists are from literally murderous non-state actors.
Kyle Pope of the Columbia Journalism Review outlines the varying (and vastly unequal) threats around the world. He focuses on Russia, where Wall Street Journal reporter Evan Gershkovich is a victim of Vladimir Putin’s ego and the fragility of the Russian military, but he sets that into a global context. “The fact is that journalism and democracy are in retreat around the world, including in the United States. The Committee to Protect Journalists, in its annual tally, reported that at least sixty-seven journalists and media workers were killed in 2022, the highest number in four years and a 50 percent jump from the previous year,” Pope writes. “Nearly as many journalists were killed in Mexico as in Ukraine.”
Thankfully, threats to journalists’ lives are not as much an issue in the United States (though isolated assassinations have occurred, such as that last year of Jeff German of the Las Vegas Review-Journal). But other threats to American journalism are more subtle, including such matters as technological change and economic forces that are killing newspapers nationwide, as well as efforts by DeSantis and others to change laws that have protected journalism. As Pope notes, DeSantis “has proposed a series of measures that hobble reporters’ ability to do their jobs, including one that would ensure comments made by anonymous sources would be presumed false in defamation lawsuits.”
Pope also notes that threats to the media come from within, from a decline in credibility. He points to Fox’s settlement with Dominion Voting Systems, suggesting that Fox News had “essentially abandoned its role as an independent chronicler of the news.” He went on: “Here we had executives and on-air anchors at the most-watched cable network in the country admitting that their devotion was more to advancing a cause—the easily disputed notion that Donald Trump had won the presidential election—than in reporting the facts. Fox’s viewers cheered the lie along. Journalism was not what they had in mind when they turned on the television.”
In that regard, it’s heartening that in the wake of embarrassing disclosures in that case Tucker Carlson is now leaving Fox. He shredded his credibility by publicly embracing Trump while privately saying he hated the man “passionately” and calling the voter fraud claims “insane.”
Yes, there are bad actors in journalism as in any other field. Carlson’s departure suggests that the marketplace — when it includes the proper functioning of the legal system — gets things right, at least over time.
Matters of life and death are at stake in censorship. State restrictions and their cousins — efforts to rewrite the past — ill serve history and the lessons we can learn from it. Some governments have sought to maintain private histories at times (one thinks of The Pentagon Papers), presumably with plans to keep such accounts secret until some undisclosed time in the future. But such efforts risk bias by the authors and deprive the public of vital information on a timely basis.
Leaders of all sorts, though particularly government officials, are threatened by free expression, of course. When the public learns of their failures, it can cost them their coveted positions, something few politicians can abide. That is why the separation of media and government must be preserved.
A Chinese colleague and I in 2016 published a study in Human Rights Quarterly, “How Chinese Journalism Students View Domestic and Foreign Media: A Survey on Credibility, Censorship, and the Role of the Communist Party in Media,” detailing how idealistic young people in China at the time valued independent thought and the freedom to publish information. Since then, the leashes have been tightening around journalism there and elsewhere and, while that may serve politicians in the short run, it shortchanges the citizens of particular countries and the world.
For a couple decades, Paris-based Reporters Without Borders has published a World Press Freedom Index that assesses the state of journalism globally. In 2022, it ranked 180 nations and territories based on the health of their media environments. Some of the results are surprising (the United States, for instance, placed 42nd, with the group explaining that “chronic issues impacting journalists remain unaddressed. These include the disappearance of local newspapers, the systematic polarisation of the media, and the erosion of journalism by digital platforms amid a climate of animosity and aggression towards journalists, among others.”) Other results are more predictable: China placed 175th and Hong Kong fell 68 places to 148th, as a result of Beijing’s crackdown there. Russia ranked 155th.
Citizens across the globe are hurt when press freedom suffers. Britain, now ranked 24th in the world index, taught the world that centuries ago. It’s a lesson best never forgotten.